Dermatologists Advise On The Best Way To Treat Melasma
- Posted on Nov. 7, 2023
- Health
- Views 78
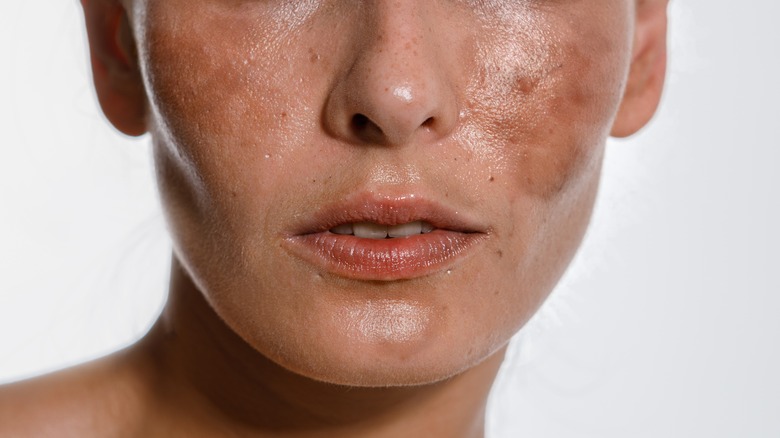
Melasma is a common skin condition that looks like brown or grayish stains on the skin. Most commonly, the disease affects a woman’s face. Despite the condition concerns many patients, reducing self-esteem, today the medicine offers plenty of treatment methods.
Read More

Understanding Melasma
The spread of the condition hugely depends on the region, affecting from 1% to 30% of. Population depending on the state. Another risk group are pregnant women. It is also more common among the people with dark skin shades, including light-brown skin. However, it can persist for years or even become a lifelong concern. Without proper protection, especially from the sun rays, the condition may return, even after right medication.
Signs of Disease
In addition to visible signs, it is identified by several characteristics:
- Dark Skin: Melasma stains look darker than the surrounding skin.
- Bilateral Appearance: The signs may appear on both sides of the face.
- Coverage Across a Large Area: Melasma can affect significant portions of the face.
- Variable Visibility: Certain areas of the face may display melasma more prominently than others.
Medication and Cosmetology Against for Melasma
Dermatologists recommend a range of skin treatments to address melasma, but good protection from the sun is a fundamental component. Even while using topical and oral treatments, exposure to sunlight can reverse progress. Sun prevention measures include:
- Mineral Sun Protection Cream: Choose a sunscreen with SPF 30+ known to block harmful UV rays.
- Hats and UV-Protective Clothing: Additional protection can be achieved through the use of hats and clothing designed to shield agains UV.
- Avoid Sun: Limit time spent in direct sunlight.
Hydroquinone
Another popular component is hydroquinone – it’s a beaching chemical that lightens the skin. However, its usage needs careful oversight to avoid uneven pigmentation.
Tretinoin
Tretinoin, derived from vitamin A, can be combined with mild corticosteroids as another option. Tretinoin aids in pigment reduction by increasing skin cell turnover and blocking melanin synthesis. While the exact mechanisms behind corticosteroid improvement in melasma are unclear, their combination with tretinoin is noted to produce synergistic effects while minimizing irritation. Long use of corticosteroids should be avoided due to the risk of skin thinning.
Creams
For cases requiring a more comprehensive approach, triple combination creams come into play, containing multiple bleaching agents. A notable example is Tri-Luma, which has FDA approval for treating melasma. Comprising 0.01% fluocinolone acetonide, 4% hydroquinone, and 0.05% tretinoin, Tri-Luma disrupts melanin production.
Acid
Supplementing topical treatments, individuals who don't see desired results can incorporate oral tranexamic acid. This oral medication inhibits melanin production and the transfer of melanin to keratinocytes, the skin cells responsible for pigment retention. When used in conjunction with topical treatments like a triple combination cream, oral tranexamic acid can help prevent melasma development and achieve an even complexion. Take note that some studies have shown its effectiveness, others suggest a potential relapse of melasma after discontinuation, necessitating further research into its long-term benefits.
Peeling
Chemical peels have been effective in promoting the growth of new, healthier skin. They act by removing discolored, dead skin layers to reveal fresher skin. These methods often complement other treatments like the triple combination cream, offering enhanced results in reducing hyperpigmentation.
Micropeeling
Microneedling, a minimally invasive technique involving fine needles to create channels in the skin, aids in deeper penetration of pigment-fighting ingredients while stimulating the skin's natural healing process. The derma renewal following microneedling helps reveal fresher, healthier skin. This method is supported by research showing its potential to achieve better results in treating melasma compared to using skin lightening agents alone.
Plasma
Another emerging option is platelet-rich plasma (PRP), which involves applying an individual's concentrated growth factors to the skin. This approach has shown effectiveness in combination with microneedling for melasma treatment, as indicated by a recent meta-analysis of studies involving adults with melasma.
Melasma Causes
Various reasons may affect the development of condition:
- Genetics: Approximately a half of patients report a family history of the disease, emphasizing a genetic predisposition.
- Sunlight: UV radiation can lead to cell membrane damage and free radical production, leading to the condition progression.
- Thyroid Disease: Thyroid issues may heighten the risk of melasma. Although treating thyroid disease can sometimes alleviate the situation, the relationship between the two requires further study.
- Medications: Particular medications, including anti-seizure drugs, oral contraceptives, and drugs sensitizing the skin to sunlight, may cause the disease.
How to Live with It?
While melasma itself is not dangerous, its appearance may resemble skin diseases. Therefore, it's essential to address a professional to prevent the disease and prescribe the medication .
The duration of treatment varies from person to person. However, many cases require intervention to reduce hyperpigmentation.