Varieties of Hearing Aids: Selecting the Appropriate Option
- Posted on Nov. 7, 2023
- Health
- Views 59
Approximately 48,000,000 Americans experience problems with hearing loss, yet only a fifth of those who could benefit from a listening aid actually use one, reports the Hearing Loss Association of America (HLAA).
Read More

Georgine Ray, an audiologist and owner of Affiliated Audiology Consultants, says: “In the mid-nineties, hearing aids started using digital processors that allowed cleaner, improved sound. Another big change is the ability to stream and use Bluetooth technology to connect wirelessly to audio on smartphones, television, and other electronic devices.”
What Is a Listening Device?
A hearing aid is a small electronic device designed to amplify sound for individuals with auditory diseases. It typically comprises a microphone, amplifier, and speaker. This device picks up sound waves, converts them into electrical signals, processes and enhances these signals, and then converts them back into sound waves for improved listening and speech comprehension.
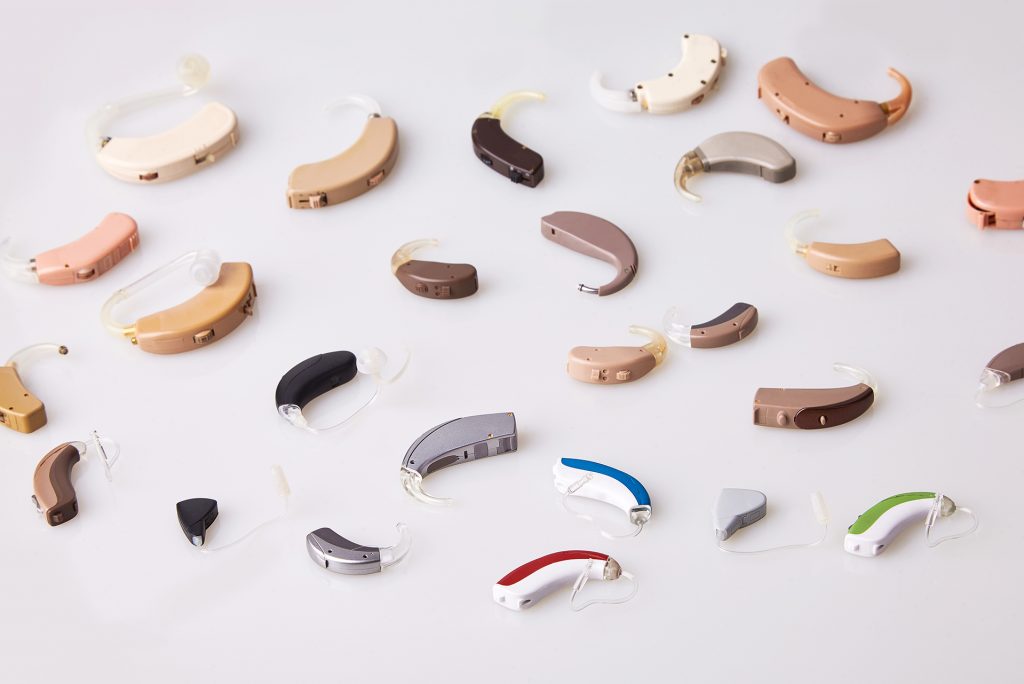
Varieties of Hearing Aids
Behind-the-Ear (BTE)
This device looks like a plastic element behind one of your ears. It contains all the necessary elements, and suits for all types of sound perception loss, except for the difficult cases.
- Pros: Suitable for mild to profound loss, offers more room for controls, available in various colors.
- Cons: More visible, potential issues with wearing glasses.
Receiver-in-Canal (RIC)
This is the most popular variation thanks to its convenience – the small devices will be placed right into your ear canal.
- Pros: Popular and less visible than BTE, available in rechargeable models.
- Cons: Insertion difficulties for some, smaller models might lack device-level volume control.
In-the-Ear (ITE)
Developed for difficult cases of her loss, this device is put inside the outer part of the ear.
- Pros: Ideal for mild to severe hearing loss, provides manual controls, and often includes telecoils and rechargeable accumulator.
- Cons: More visible than other custom types, potential comfort issues.
In-the-Canal (ITC)
This is a plastic box placed in the hearing canal, suitable for customers with mild and severe diseases.
- Pros: Suitable for mild to severe loss, has bigger batteries for easier handling, less visible than larger custom ITEs.
- Cons: Limited space for components, more visible than smaller in-canal aids.
Completely-in-Canal (CIC)
These are individually-made devices that should perfectly fit the form of the canal.
- Pros: Nearly invisible on many ears, suitable for mild to moderate loss.
- Cons: The smallest battery seems difficult to handle, and requires more user maintenance, potential discomfort, and sound quality issues.
Invisible-in-Canal (IIC)
The smallest type, this one sits in the ear but remains fully invisible to other people.
- Pros: Nearly invisible, cosmetic appeal, and minimal interference while using the telephone.
- Cons: Similar to CIC, users may face voice-related issues.
Extended-Wear Aids
This type is rather a professional instrument, developed for patients who need constant support. The device is put deep inside the ear by the professional, and cannot be put outside without assistance.
- Pros: Completely invisible, comfortable, extended battery life.
- Cons: Requires professional placement, unsuitable for certain ear conditions, no wireless connectivity
Additional Features
Various hearing instruments come with different features such as directional microphones, telecoils, remote microphones, feedback suppression, noise reduction, rechargeable batteries, wireless connectivity, remote controls, smartphone apps, and preset settings for different environments.
Consulting a hearing care professional is crucial when selecting a hearing aid. Seeking their expertise is vital for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment, ensuring effective solutions for hearing challenges. Georgine Ray, an audiologist, emphasizes the necessity of expert input to address hearing loss adequately.