Schizophrenia: Symptoms and Treatment in 2023
- Posted on Nov. 7, 2023
- Health
- Views 62
Schizophrenia is a severe mental health disorder, occuring in all ages and in different forms. It influences the personal and professional life of the patient, and becomes a significant part of one’s life. Luckily, today’s patients have a wide range of medication and therapy solutions. Furthermore, the understanding of diagnosis significantly improved during the last decades.
Read More
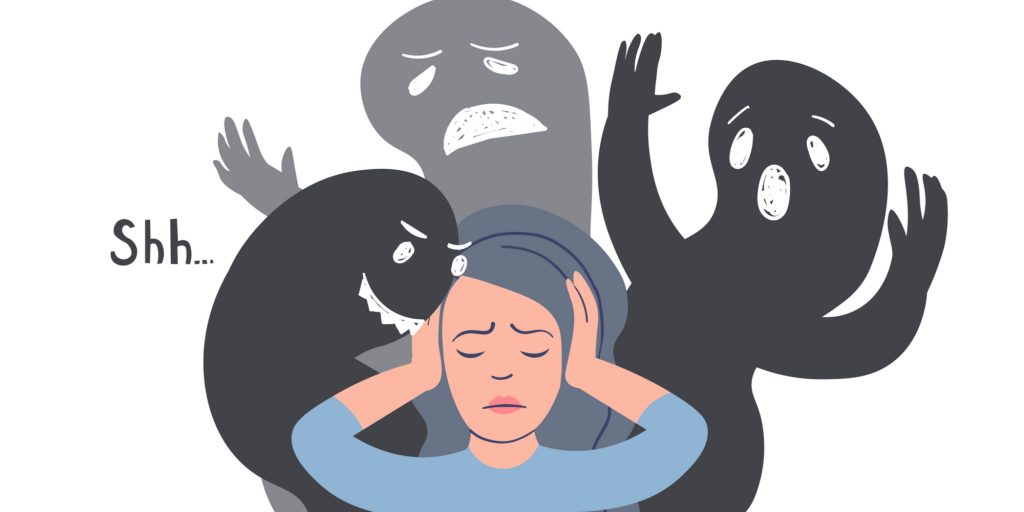

What Should Everyone Know About the Diagnosis
Schizophrenia is characterized by delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized thoughts, and is extremely rare, affecting only 1% of the population. Even in the light form, the disease should be treated seriously – the best idea is to start medication as fast as possible.
Types of Schizophrenia
While previous editions of diagnostic manuals categorized schizophrenia into subtypes, the current DSM-5 defines it as a spectrum disorder, including five primary classifications:
- Paranoid Type: Characterized by delusions or hallucinations without disorganized behavior or speech.
- Disorganized Type: Involves disorganized speech and behavior with flat or inappropriate affect.
- Catatonic Type: Displays various behavioral extremes, from loss of sensation or consciousness to hyperactivity.
- Undifferentiated Type: Presents symptoms of schizophrenia without fitting into specific subtypes.
- Residual Type: Involves odd beliefs or unusual experiences without delusions or hallucinations.
Signs and Symptoms
Schizophrenia episodes disrupt an individual's reality perception, making it challenging to differentiate between real and imagined experiences. Common symptoms include:
- Impaired daily functioning
- Hallucinations (auditory, visual, tactile, taste, or olfactory)
- Delusions that resist factual evidence
- Disorganized thinking and behavior
- Negative symptoms like loss of motivation and interest
The DSM-5 guidelines necessitate the experience of at least two of these symptoms within one month for a formal schizophrenia diagnosis, with hallucinations, delusions, or disorganized thinking as the minimum requirement.
Schizophrenia Across Ages
Only 0.4% of children of the age 5-18 suffer from the diagnosis. It is much more common among adults. However, diagnosing mental health issues in teens can be challenging due to symptom overlap with other conditions, such as ADHD or trauma.
Understanding Schizophrenia's Causes
Family history, genetics, environment, the growing condition – all this can lead to the diagnosis. However, there is no one particular reason. Modern medicine doesn't know the root of the disorder, but makes everything possible for timely treatment.
Diagnosis and Misconceptions
Diagnosing schizophrenia involves assessing symptoms over several months, as there is no definitive test. Misconceptions surrounding schizophrenia often perpetuate harmful stereotypes, although research indicates that treated individuals are not inherently dangerous. The stigma may hinder individuals from seeking or adhering to treatment.
Schizophrenia Treatments
Addressing schizophrenia involves a comprehensive approach combining medication, therapy, lifestyle changes, community support, and ongoing care. Medications include antipsychotics, categorized as first and second-generation, which help alleviate symptoms and prevent reoccurrences.
Medication
There are two main types of medication, the choice of which depends on the patient’s condition. Antipsychotics of the first type block the dopamine in the brain. These drugs include:
- Chlorpromazine
- Fluphenazine
- Haloperidol
- Loxapine
- Perphenazine
The main distinction of the second-generation medication is that it locks both dopamine and serotonin receptors. Among them are:
- Aripiprazole
- Asenapine
- Clozapine
- Iloperidone
- Lurasidone
Seeking Help
Receiving professional help when psychosis symptoms arise is crucial. Close relatives or teachers often notice symptoms first. Early intervention within the first two years of symptom onset leads to improved outcomes, with complete recovery being a possibility.
Schizophrenia necessitates lifelong treatment, and leaving it untreated may exacerbate symptoms, impacting daily functioning and potentially leading to increased depression or suicidal thoughts. If someone is experiencing psychosis symptoms, seeking professional help promptly is advised.
By being aware of the symptoms, understanding the potential causes, and seeking appropriate professional support, individuals can manage schizophrenia effectively and lead fulfilling lives.