Diabetes Symptoms: Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational Varieties
- Posted on Nov. 7, 2023
- Health
- Views 77
In contemporary society, diabetes stands as a common health challenge, impacting an estimated one in ten individuals. Across the U.S., this translates to over 34 million people grappling with this condition, while an additional 88 million adults are on the cusp of diabetes, dealing with what's known as prediabetes. These statistics underscore the critical importance of recognizing the signs of diabetes to manage it effectively and mitigate its potentially severe health repercussions.
Read More
The Essence of Diabetes
Diabetes is essentially a cluster of conditions where there's an overload of sugar in the bloodstream. It's all due to the body's struggle to either produce enough insulin or properly use the insulin it produces. Insulin serves as the key that unlocks cells, permitting glucose to enter and be used as fuel. When this process falters, glucose accumulates in the blood, setting the stage for a host of health issues.
Diabetes is not a monolithic condition; it presents in several variants. Type 1 diabetes, although less common, typically manifests in the younger demographic and involves an autoimmune response that halts insulin production entirely. While the search for a cure continues, those with type 1 diabetes must rely on insulin therapy for survival.
Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is more widespread and continually associated with lifestyle aspects such as diet and bodily workout. This type involves opposition to insulin or insufficient insulin production and can sometimes be managed or even reversed with lifestyle modifications.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The identification of diabetes symptoms is pivotal, as early detection can significantly improve management outcomes. The symptoms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes can overlap but often differ in their intensity and onset.
Type 1 Diabetes: The Warning Signs
Children, teenagers, and young adults are primarily the ones diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. The symptoms can be abrupt and severe, including:
- Constant thirst and increased urination as the body attempts to eliminate excess sugar.
- Unexpected weight loss, despite normal or increased food intake.
- A notable increase in hunger is due to the body’s inability to use glucose properly.
- Fatigue, which is a result of insufficient sugar entering the cells.
- Cuts or bruises that heal slowly, are a consequence of high blood sugar levels affecting circulation and the healing process.
- Changes in vision due to high glucose levels alter the fluid levels in the eyes.
Type 2 Diabetes: Subtle and Sneaky Signs
Type 2 diabetes often creeps in silently, with symptoms that may be so mild they go unnoticed for years. These can include:
- Slight increases in thirst and urination compared to the more dramatic symptoms of type 1 diabetes.
- Hunger, even after eating, because of the inefficient use of glucose.
- General fatigue as the body struggles to convert glucose into energy.
- Blurry vision, not as acute as in type 1, but still noticeable.
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet, signaling nerve impairment from high blood sugar levels.
- Wounds that heal slowly, similar to type 1 diabetes.
There may be even more, a healthcare provider may give insights.
The Gestational Diabetes Concern
A unique form of diabetes, gestational diabetes, emerges during pregnancy. It's often asymptomatic, detected through routine screenings rather than symptomology. On occasion, symptoms akin to those of type 2 diabetes may surface, such as increased thirst or frequent infections.
The Path to Diagnosis
Identifying diabetes often begins with an awareness of its potential signs, followed by clinical screening. Currently, recommendations advise that adults, particularly those who are overweight, begin screening at age 35 and repeat it periodically.
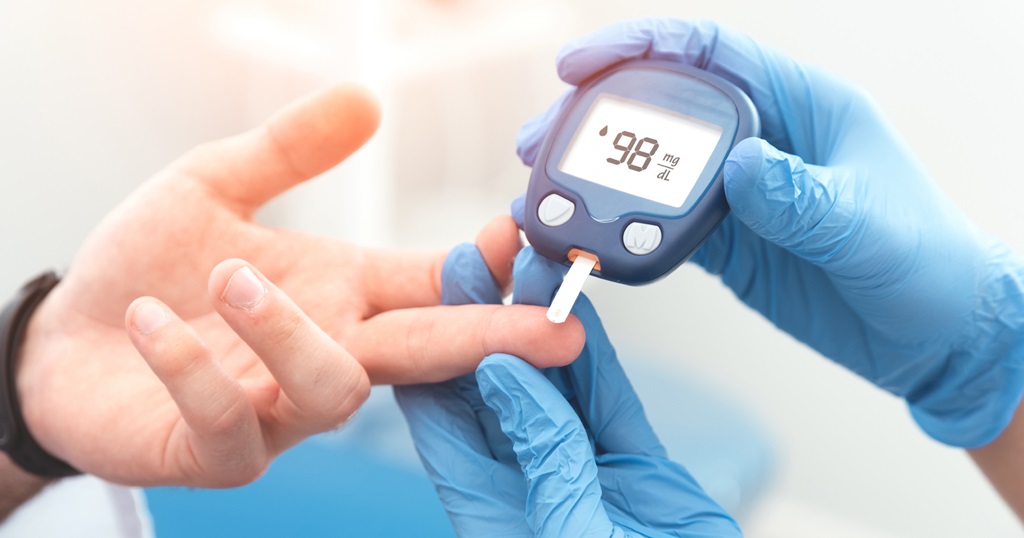
Diagnosis can be achieved through several blood tests, with the A1C test offering a moderate blood sugar station over months, and fasting plasma glucose and accidental plasma glucose tests providing snapshot assessments.
Taking Action
Knowing what's up and acting fast is key to tackling diabetes. Getting a precise diagnosis is step one. After that, you can begin strategies to manage it. Doing so really lowers the odds of serious health issues down the road and puts you on track for a healthier, fuller life.
People can effectively manage diabetes by gaining sufficient knowledge about the condition, making healthy lifestyle choices, and accessing the necessary medical support. This lets them keep living their lives with quality and feeling good.